Alert
Alerts
The Causse Loop (by mountain-bike)





Description
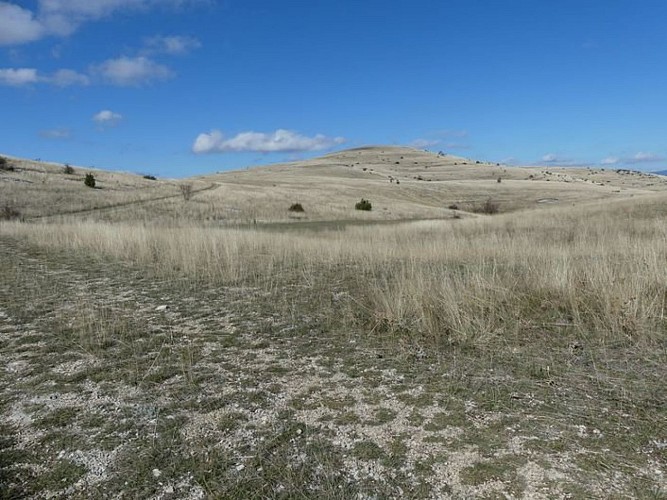
The plateau of the Causse Méjean seems to stretch out forever. But appearances can be deceptive! This flatness conceals a number of short steep climbs.
Mountain-bike route # 2. From the Col de Pierre Plate, go down a small technical descent to join up with the road leading to Le Tomple. Go through the hamlet and continue to La Condamine. At the crossroads with the road going towards Montbrun, go left for a few metres, then turn right onto a small path. Join up with the track leading to Fraissinet-de-Poujols. Go through the hamlet and turn right towards Poujols. Continue straight all the way to Chaldas. After Chaldas, at Point 1015, take the path going downhill to Chamblon. Go into the hamlet and continue on the road (GR 60) and then on the track (GR 60). Cross the D 16 and skirt Le Fraisse farm to get to Nivoliers. In Nivoliers, head towards Cavaladette on a former village track. Below Cavaladette, take the road and, at the cross, turn right onto the track leading to Cavalade, Cros Roux, Cros Garnon. In Cros Garnon, pass in front of the church before going first to La Mecoire and then to Valbelle. Take the D 16 for 3 km to return to the car park at the Col de Pierre Plate.
Technical Information
Altimetric profile
Starting point
Points of interest
Additional information
Departure
Col de Pierre Plate pass
Arrival
Col de Pierre Plate pass
Ambiance
This trail is entirely on the Causse Méjean. It goes through the steppe-like landscape that is specific to the Causses plateaux. Natural Scots-pine forests and planted black-pine forests dot the route and bring some shade. You can see handsome traditional farms and typical hamlets built entirely from limestone.
Access
From Florac, drive up the D16 to the car park at the Col de Pierre Plate pass
Advised parking
Car park at the Col de Pierre Plate
Advice
No cycling off-track. Trails are stony and at times steep. You are strongly advised to wear a helmet. Do not forget your repair kit and a small set of tools. Be careful around flocks and dogs. Please shut all gates and barriers behind yourself. Slow down in farms and hamlets. Carry water.
Is in the midst of the park
The national park is an unrestricted natural area but subjected to regulations which must be known by all visitors.
Data author